Upon his victory over the Medes, he founded a government for his new kingdom, incorporating both Median and Persian nobles as civilian officials. The conquest of Asia Minor completed, he led his armies to the eastern frontiers. Hyrcania and Parthia were already part of the Median Kingdom. Further east, he conquered Drangiana, Arachosia, Margiana and Bactria. After crossing the Oxus, he reached the Jaxartes, where he built fortified towns with the object of defending the farthest frontier of his kingdom against nomadic tribes of Central Asia.
The victories to the east led him again to the west and sounded the hour for attack on Babylon and Egypt. When he conquered Babylon, he did so to cheers from the Jewish Community, who welcomed him as a liberator- he allowed the Jews to return to the promised Land. He showed great forbearance and respect towards the religious beliefs and cultural traditions of other races. These qualities earned him the respect and homage of all the people over whom he ruled.
 |
| Bas-Relief of Cyrus the Great, in Pasargad, Iran |
The victory over Babylonia expressed all the facets of the policy of conciliation which Cyrus had followed until then. He presented himself not as a conqueror, but a liberator and the legitimate successor to the crown. He also declared the first Charter of Human Rights known to mankind. He took the title of “King of Babylon and King of the Land”. Cyrus had no thought of forcing conquered people into a single mould, and had the wisdom to leave unchanged the institution of each kingdom he attached to the Persian Crown. In 539 BCE he allowed more than 40,000 Jews to leave Babylon and return to Palestine. This step was in line with his policy to bring peace to Mankind. A new wind was blowing from the east, carrying away the cries and humility of defeated and murdered victims, extinguishing the fires of sacked cities, and liberating nations from slavery.
Cyrus was upright, a great leader of men, generous and benelovent. The Hellenes, whom he conquered regarded him as ‘Law-giver’ and the Jews as ‘the annointed of the Lord’.
Prior to his death, he founded a new capital city at Pasargade in Fars. and had established a government for his Empire. He appointed a governor (satrap) to represent him in each province, however the administration, legistlation, and cultural activities of each province was the responsibility of the Satraps. Accoding to Xenophon Cyrus is also reputed to have devised the first postal system, (Achaemenide achievements). His doctrines were adopted by the future emperors of the Achaemenian dynasty.
 Cyropaedia of Xenophon, The Life of Cyrus The Great
Cyropaedia of Xenophon, The Life of Cyrus The Great
Xenophon (Greek mercenary & historian 430 – 355 BCE).
 Achaemenid Army
Achaemenid Army
By: Professor A. Sh. Shahbazi
 Cyrus the Great: The decree of return for the Jews, 539 BCE
Cyrus the Great: The decree of return for the Jews, 539 BCE
Edited by: Charles F. Horne
 The Cyrus the Great Cylinder
The Cyrus the Great Cylinder
The first known Charter of Rights of Nations, 539 BCE.
Edited by: Shapour Ghasemi
 The History of Herodotus, (485 – 425 BCE)
The History of Herodotus, (485 – 425 BCE)
A reference of Persian Empire’s history ofAchaemenian era.
 Old Persian Cuneiform
Old Persian Cuneiform
The official script of the Achaemenid Empire







 Candle Holder
Candle Holder Coasters
Coasters Jewelry Box
Jewelry Box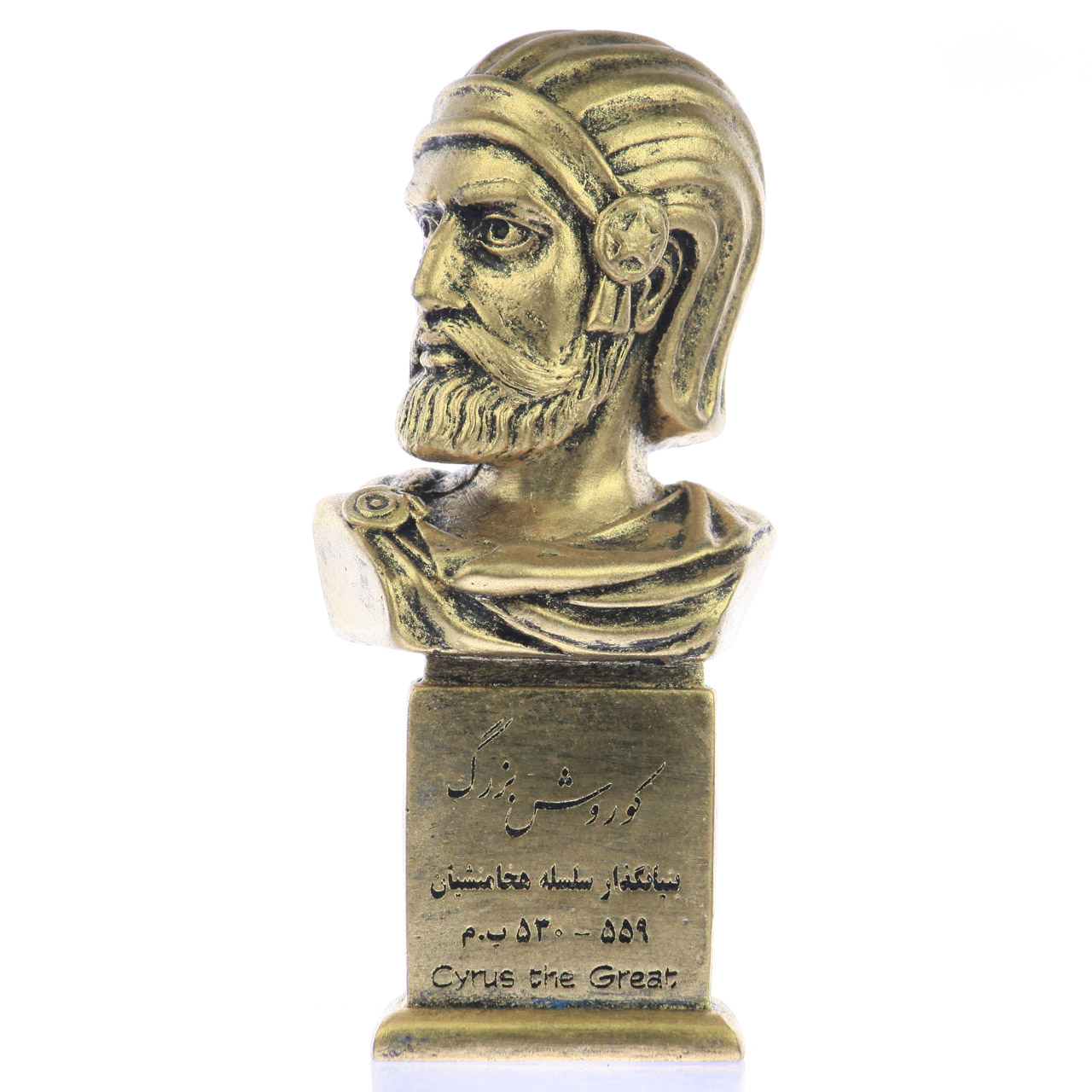
























Reviews
There are no reviews yet.